Difference between revisions of "Linuxstamp"
| (130 intermediate revisions by 27 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Image:linuxstamp_top_02.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | The Linuxstamp is designed to be a general purpose processor module. It is designed to work as a stand alone module (SD card, | + | The Linuxstamp is designed to be a general purpose processor module. It is designed to work as a stand alone module (SD card, Ethernet and USB/Serial converter are all on the module). This allows all initial development to be done without a motherboard, but for integration into a specific project a motherboard with specific features could be designed. Check out the start of the first mother board for the Linuxstamp, [http://opencircuits.com/Linuxstamp_Mboard_1 Mboard 1]. |
| + | |||
| + | == Status == | ||
| + | You can now purchase Linuxstamp boards from [http://thelinuxstamp.com/shop/catalog/browse?shop_param= thelinuxstamp.com] | ||
== Features == | == Features == | ||
| − | * Atmel AT91RM9200 processor (Arm9 processor with MMU) | + | * Atmel AT91RM9200 processor (Arm9 processor with MMU, 180Mhz operation) |
* 32MB SDRAM (Only limited by 1x 54-TSOP SDRAM chip) | * 32MB SDRAM (Only limited by 1x 54-TSOP SDRAM chip) | ||
* 8MB SPI Dataflash | * 8MB SPI Dataflash | ||
| Line 14: | Line 19: | ||
* POE capable (48v -> 5v Power supply can be implemented on a motherboard) | * POE capable (48v -> 5v Power supply can be implemented on a motherboard) | ||
| − | == | + | == License == |
All files for this project are licensed under the GNU GPL V2 | All files for this project are licensed under the GNU GPL V2 | ||
| − | == | + | == Hardware design files == |
| − | Warning!!! | + | Warning!!! Use this design at your own risk. |
| − | * [[ | + | * [http://linuxstamp.budgetdedicated.com/index.php?dir=&file=linuxstamp_design.zip Project zip file] |
| − | * [ | + | * [http://linuxstamp.budgetdedicated.com/index.php?dir=&file=linuxstamp121-sch.pdf Schematic] |
| − | + | * [http://linuxstamp.budgetdedicated.com/index.php?dir=&file=linuxstamp121-top.pdf Top layer] | |
| − | + | * [http://linuxstamp.budgetdedicated.com/index.php?dir=&file=linuxstamp121-bottom.pdf Bottom layer] | |
| + | If you want to use the Linuxstamp for your project you can get an Eagle library file [http://linuxstamp.budgetdedicated.com/index.php?dir=&file=linuxstamp.lbr here] | ||
| + | or just an image [http://linuxstamp.budgetdedicated.com/index.php?dir=&file=headers.PNG here] | ||
== Power == | == Power == | ||
| − | The power supply for the board is based on the Linear LTC3407-3. This is a very compact high frequency switching power supply. It has both a 3.3v and a 1.8v output. It does have a very tight input range 3.3v-5.5v. The Micrel PHY also needs 2.5v, but this is provided by an internal regulator. Currently a regulated 5v must be used to power the board. Talking with Jeff from Jendy Labs it seems like POE (Power Over Ethernet) is a good idea. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_over_Ethernet | + | The power supply for the board is based on the Linear LTC3407-3. This is a very compact high frequency switching power supply. It has both a 3.3v and a 1.8v output. It does have a very tight input range 3.3v-5.5v. The Micrel PHY also needs 2.5v, but this is provided by an internal regulator. Currently a regulated 5v must be used to power the board. Talking with Jeff from Jendy Labs it seems like POE (Power Over Ethernet) is a good idea. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_over_Ethernet Wikipedia] has a good general description of POE. The basic idea is that POE provides 48v and up to 13 watts, more than enough power for the Linuxstamp. The problem for the module is that a 48v -> 5v power supply is not small or cheap. In order to take advantage of POE without increasing the board size I found a part from Transtek Magnetics that is made for POE and has the rectifier built into the jack. The 48v lines are then connected to the pin header. This will allow a motherboard to integrate a POE power supply. |
| + | |||
| + | == Minicom & the debug port == | ||
| + | The mini-USB device port on the Linuxstamp does not connect directly to the AT91RM9200 it connects to the FT232R chip. The FT232R is a USB/serial converter. The FT232R chip has drivers for both Windows and Linux, but the Linux drivers are included in later kernels. Drivers for Mac OS X are available [http://www.ftdichip.com/FTDrivers.htm here]. | ||
| − | == | + | When you plug the Linuxstamp into your host (Linux) machine a device should appear '''/dev/ttyUSB0''' (I think the postfix number will increment as you add more devices). '''/dev/ttyUSB0''' will behave as any other serial port now. '''Minicom''' is the standard program to access the serial port in Linux. The first time you run minicom you will have to be root in order to do the setup, after that you can change the permissions on /dev/ttyUSB0 so any user can run minicom. To enter configuration mode in minicom type '''CTRL-A o''', now scroll down to '''Serial port setup'''. Use the letters to navigate. You will want the device to be '''/dev/ttyUSB0''' and '''Bps/Par/Bits''' to read '''115200 8N1'''. Both hardware and software flow control should be OFF. Connection to the board is important for loading Atmel's tiny program and u-boot, but once the board is working it might not be as important. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The default installation of minicom does not automatically include the XModem file transfer module 'sx' which you will need to send files. It is part of the Linux package named lrzsz ([http://packages.debian.org/lenny/lrzsz lrzsz]). Just type 'sx' at a command line to see if it is installed. If not, install the lrzsz package and minicom will find and use 'sx' automatically. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | XModem transfers between Minicom and U-Boot seem to work fine. This means that you can update U-Boot itself as well as the kernel and root file systems using Minicom after getting U-Boot itself installed via the built-in hardware bootloader in the AT91RM9200. The bootloader is much more finicky than U-Boot itself, so getting U-Boot installed can be tricky. Here is my technique: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Connect the USB cable to LinuxStamp and start minicom from a terminal window. | ||
| + | * Boot the LinuxStamp. You should see CCC... on the minicom console, with a new C every second or two. | ||
| + | * Hit Enter twice. This will stall the bootloader, and the CCC... sequence will stop. It will also synchronize the USB/serial converter. | ||
| + | * Hit Ctrl-A Z S sequence to bring up the file transfer dialog in minicom. Select XModem and navigate to and select your u-boot.bin file (space bar). | ||
| + | * Hit Enter to start the xmodem transfer in minicom. | ||
| + | * Press and release the reset pushbutton on the LinuxStamp. The transfer should happen very quickly (a few seconds). | ||
| + | * Immediately hit Enter twice when you see the transfer complete. You *must* do this very quickly (within 1 second or so), and you *must* hit Enter twice. The first time exits the minicom file tranfer dialog, and the second time stalls the newly-loaded U-Boot program so that it doesn't try to auto-run the not-yet-loaded Linux kernel image. | ||
| + | |||
| + | You now have U-Boot in RAM, but not yet in flash. However, U-Boot is a lot nicer than the hardware bootloader, so you can now use U-Boot to load itself into flash by using the U-Boot menu and retransferring the u-boot.bin file again. This second time, the transfer will end up in flash, and will persist through poweroff/on. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Another alternative is to use HyperTerm on Windows, which works fine with the Hardware boot loader. If you are updating the Darrel Bootloader, note that the loader only has a short delay after you initiate the "receive" (on the loader) after which it send out the "ready to receive" signal. As a result, you'll need to be rather quick to initiate the Xmodem "send" (on HyperTerm). If you are seeing time outs on HyperTerm when you try and send the loader.bin file, you are probably hitting this problem ... you need to have initiated the send before you see the "C" on the screen from the bootloader. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == nfs & tftp == | ||
| + | Nfs (network file system) and tftp (trivial file transfer protocol) are two servers you will want running on your host machine. Nfs is useful for hosting the root file system of the Linuxstamp. Tftp is useful for u-boot to retrieve the kernel from. There are many other websites on nfs and tftp, but I will try and go over a simple setup. I would suggest being behind a firewall before trying either of these setups as neither is secure. I wrote this using a Fedora 7 system. First make sure you have nfs installed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | $ '''yum install nfs-utils nfs-utils-lib portmap system-config-nfs''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | On Ubuntu (or other debian-style systems) you could use: | ||
| + | |||
| + | $ '''sudo apt-get install portmap nfs-kernel-server nfs-common''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now to make sure the service is enabled run (this won't work on Ubuntu): | ||
| + | $ '''serviceconf''' and make sure '''nfs''' and '''nfs lock''' are checked | ||
| + | Now edit '''/etc/exports''' you should add a line like this '''/path_to_nfs_root/ *(rw,no_root_squash,insecure)'''. Now restart nfs. | ||
| + | $ '''sudo /etc/init.d/nfs restart''' | ||
| + | You can test that it is set up correctly by typing the following on the local system (i.e. right on the NFS server) | ||
| + | $ '''showmount -e localhost''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can test this from a remote system with | ||
| + | $ '''mount -t nfs server_name:/path_to_nfs_root /path_to_test_mount''' | ||
| + | Now on to tftp. Make sure it is installed. | ||
| + | $ '''yum install tftp-server''' | ||
| + | This will create a file '''/etc/xinetd.d/tftp'''. In this file you will want to change '''disable''' from '''yes''' to '''no'''. | ||
| + | Now make a test file. | ||
| + | $ '''cd /tftpboot''' | ||
| + | $ '''echo hello > file''' | ||
| + | Now we can test it | ||
| + | $ '''tftp -v server_name -c get tmp''' | ||
| + | Now with u-boot we can load image files | ||
| + | > '''tftpboot 20800000 uImage''' | ||
| + | And boot them | ||
| + | > '''bootm 20800000''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Cross Compiler == | ||
| + | In order to compile for the AT91RM9200 we need to build a cross compilier. Dan Kegel has created a very useful [http://kegel.com/crosstool/ tool] for building a cross compiler. I am using Fedora 6 (x86_64) as my host system. After downloading and extracting crosstool (I was using version 0.43) I made two small changes. In the "demo-arm.sh" file I changed the eval line to | ||
| + | *"'''eval `cat arm.dat gcc-3.4.5-glibc-2.3.6.dat` sh all.sh --notest'''"<br> | ||
| + | In the "arm.dat" file I changed the TARGET to "arm-linux" (By default u-boot looks for arm-linux-* tools). Now if you run "demo-arm.sh" you should get a cross compilier. | ||
| + | |||
| + | On Debian-style-systems you need to run something like ''apt-get install build-essential bison flex'' to get the above to work. | ||
== Booting == | == Booting == | ||
| − | The AT91RM9200 has several features the | + | The AT91RM9200 has several features the facilitate easy booting. There is a good description of the booting order [http://www.open-research.org.uk/ARMuC/At91rm9200_Booting.html here]. Atmel provides a tiny [http://www.atmel.com/dyn/resources/prod_documents/uboot-DataFlash_1_01.zip program] that lives in the Dataflash and loads u-boot (see next section). |
| − | + | ||
| − | First we need | + | == U-boot == |
| − | * | + | First we need [http://www.denx.de/wiki/UBoot u-boot] (doc) [http://www.denx.de/cgi-bin/gitweb.cgi source] (git) (formerly on [http://sourceforge.net/project/showfiles.php?group_id=65938 sourceforge]) (I was using version 1.1.6 - this is an old version). If you have not yet built a cross compilier now would be a good time to do so (See the cross compilier section above). Now you can do a test for the Atmel AT91RM9200 DK board. |
| − | * | + | * $ '''make at91rm9200dk_config''' |
| + | * $ '''make''' | ||
This should give you a "u-boot.bin" file. We will have to write a board specific configuration file for the Linuxstamp. We should be able to base it off the the Atmel DK board. If you look at "/u-boot-1.1.6/include/configs/at91rm9200dk.h" you can see the configuration for the DK board. | This should give you a "u-boot.bin" file. We will have to write a board specific configuration file for the Linuxstamp. We should be able to base it off the the Atmel DK board. If you look at "/u-boot-1.1.6/include/configs/at91rm9200dk.h" you can see the configuration for the DK board. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Other u-boot commands: | ||
| + | * > '''printenv''', prints the enviroment variables | ||
| + | * > '''saveenv''', saves the enviroment variables | ||
| + | * > '''setenv bootcmd 'tftpboot 20800000 uImage; bootm 20800000'''' Sets the boot command to load a image over tftp and boot it | ||
| + | * > '''setenv bootargs mem=32M nfsroot=192.168.0.3:/nfs_root ip=192.168.0.51 console=ttyS0,115200n8 rootdelay=1''' | ||
| + | This sets the command line to be passed to the kernel. As you can see it sets the nfsroot, ip address and console | ||
| − | == | + | == Busybox == |
| − | + | [http://www.busybox.net/ Busybox] provides the necessary utilities (e.g ls, cp, etc...). After you have downloaded and unpacked busybox we are ready to get started (I was using version 1.4.2). | |
| − | * | + | * $ '''make defconfig''' |
| − | In the | + | Now for a quick test we can make busybox for our host machine |
| + | * $ '''make''' | ||
| + | After you run this you should have a file 'busybox'. Now try | ||
| + | * $ '''./busybox ls''' | ||
| + | But we want to build busybox for our embedded system so run | ||
| + | * $ '''make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-''' | ||
| + | If you want to make Busybox with all the symbolic links for the tools run | ||
| + | * $ '''make CONFIG_PREFIX=/path_to_dir ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Building the Linux Kernel == | ||
| + | If you have ever built the kernel for your desktop, then cross-compiling the kernel isn't that much harder. First get the latest kernel from [http://kernel.org/ kernel.org] (I was using 2.6.23-rc9), then get the AT91RM9200 patch from [http://maxim.org.za/at91_26.html here]. After you unpack both of these you can apply the patch. From a Fedora 11 Live install you need the following packages: gcc, gcc-c++ and qt3-devel (for xconfig). | ||
| + | * $ '''patch -p1 < 2.6.23-rc3-at91.patch''' | ||
| + | Now lets take a look at the default configurations | ||
| + | * $ '''make ARCH=arm help''' | ||
| + | The ecbat91 is the closest to the linuxstamp. | ||
| + | * $ '''make ARCH=arm ecbat91_defconfig''' | ||
| + | If we what to further customize the build we can use 'xconfig' | ||
| + | * $ '''make ARCH=arm xconfig''' | ||
| + | Now we're are ready to build the kernel. You will have to have the u-boot tool '''mkimage''' in the '''PATH''' for this to work | ||
| + | * $ '''make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- uImage''' | ||
| + | If you want to build the modules you can do | ||
| + | * $ '''make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- modules''' | ||
| + | And then if you want to install the modules to an an NFS root or somewhere else do | ||
| + | * # '''make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- modules_install INSTALL_MOD_PATH=/path_to_nfs_root/''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Minimal filesystem == | ||
| + | There isn't much you need for a minimal filesystem. I suggest creating a staging area to create the filesystem. First you need the libraries generated by the cross compiler. On my machine they are located at '''/opt/crosstool/gcc-3.4.5-glibc-2.3.6/arm-linux/arm-linux/lib'''. Next you will need busybox, and we saw in the busybox section we can tell busybox where to output the files (use the root directory of your staging area). The last file we need is '''/dev/console'''. | ||
| + | * $ '''mkdir /staging_path/dev''' | ||
| + | '''/dev/console''' is a special file used to bind a device driver to a file. As such we use the '''mknod''' command. | ||
| + | * $ '''mknod /staging_path/dev/console c 5 1''' | ||
| + | The '''c''' says this is a character device. The '''5''' is the major node, and the '''1''' is the minor node. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | For development the most convenient way to work is by mounting an NFS root file system. Another easy way to deal with the root file system is by mounting it on either a USB drive or SD card, but if you want a stand alone system you will want the root filesystem to come from the onboard Dataflash. There are several steps to do this. The Dataflash on the Linuxstamp is 8MB. A little under 2MB is used for the bootloaders and the Linux kernel. This leaves about 6MB for the filesystem. The filesystem I am working with is about 10MB, so we will need to compress the filesystem. One method of doing this is to use the initramfs function in the kernel. The kernel expects the image to be a gzipped CPIO archive. In the kernel source there are tools to create the CPIO archive. First we must create a file list from our file system (presumedly this is just the root of your current NFS mount). | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | /!!Remember that you need a 'init' file in /. You can just link to /sbin/init | ||
| + | * $ '''cd /path_to_linux_source''' | ||
| + | * # '''scripts/gen_initramfs_list.sh /path_to_fs_root/ > cpio_list | ||
| + | Next create the CPIO archive | ||
| + | * # '''usr/gen_init_cpio cpio_list > initramfs.cpio''' | ||
| + | You might have to make gen_init_cpio (in the usr dir) | ||
| + | * # '''make gen_init_cpio''' | ||
| + | Gzip the CPIO archive | ||
| + | * $ '''gzip initramfs.cpio''' | ||
| + | Now copy initramfs.cpio.gz to usr/initramfs_data.cpio.gz, and run the normal kernel make. You will notice that uImage is much larger (size = kernel + fs). | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Debian == | ||
| + | If want the full Linux enviroment your used to then you can try out Debian on the Linuxstamp. A working Debian filesystem can be found on the [http://linuxstamp.budgetdedicated.com/index.php?dir=&file=sid_20080726.tar.bz2 ftp site.] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Ptxdist == | ||
| + | If you looking for more features than the minimal filesystem, but don't need the full Debian system then ptxdist is right for you. The folks over at [http://www.pengutronix.de/ Pengutronix] have done a very good job creating [http://www.pengutronix.de/software/ptxdist/index_en.html Ptxdist], a simple tool for building an embedded Linux distribution. If you want to test it out with the Linuxstamp, you can grab a build of the [http://linuxstamp.budgetdedicated.com/index.php?dir=&file=ptxroot_linuxstamp_20090124.tar.bz2 filesystem] and [http://linuxstamp.budgetdedicated.com/index.php?dir=&file=uImage_ptx_2.6.27_20090124 kernel]. If you want to try out ptxdist yourself, you can get the Linuxstamp project [http://linuxstamp.budgetdedicated.com/index.php?dir=&file=ptx_linuxstamp_pjt_20090124.tar.bz2 here]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Dropbear SSH == | ||
| + | One of the first non busybox tools you will want is SSH. Dropbear is a small SSH client/server. I was able to get version 0.50 working. | ||
| + | *[http://matt.ucc.asn.au/dropbear/dropbear.html http://matt.ucc.asn.au/dropbear/dropbear.html] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | * $ '''./configure --host="arm-linux" --disable-zlib --prefix=/staging_path''' | ||
| + | * $ '''make all''' | ||
| + | * # '''make all install''' | ||
| + | You will have to make the device nodes '''/dev/ptmx''' and '''/dev/tty''' | ||
| + | * # '''mknod /dev/ptmx c 5 2''' | ||
| + | * # '''mknod /dev/tty c 5 0''' | ||
| + | You will also have to have the devpts filesystem mounted. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == 802.11 Wireless Networking == | ||
| + | With the 2.6.27 vanilla kernel the ralink USB driver works very well. I've been using the AZIO AWU254 without any problems. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == GPIO / Hardware Pin I/O == | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you need some guidance figuring out how to 'bit twiddle' the GPIO (General Purpose I/O) pins on the at91 processor, here is a simple example with make file. If you have your arm-linux cross compiler configured with CrossTool just unpack this file into a folder and type 'make' to generate the executable binary. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [http://linuxstamp.budgetdedicated.com/downloads/at91_gpio_example.zip at91_gpio_example.zip] | ||
| + | |||
| + | This example shows how to set and clear output pins read input pins. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Servos == | ||
| + | [[Image:Servos.jpg]] | ||
| − | == | + | It is very easy to use the Linuxstamp with a RC servo controller like this one from [http://www.pololu.com/catalog/product/208/pictures pololu]. In this setup the board is powered from the USB connector, so I was able to use the power terminal to power the pololu module. On the under side of the pololu module I connected the servo power with the chip power. The only other thing that is needed is the serial TX line from the Linuxstamp (yellow wire). I created a very simple [http://linuxstamp.budgetdedicated.com/index.php?dir=&file=servo_test.tar.bz2 program] to run the servos. The following example would set servo 0 to a speed of 54 (64 is stopped) with an acceleration of 2. |
| − | + | *'''# ./servo_ser 0 2 54''' | |
| − | * | ||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
| Line 54: | Line 198: | ||
*[http://cadsoft.de/ Cadsoft.de]: Free (as in beer) tools for schematic and PCB design | *[http://cadsoft.de/ Cadsoft.de]: Free (as in beer) tools for schematic and PCB design | ||
*[http://openhardware.wordpress.com/ openhardware.wordpress.com]: Here is my openhardware blog | *[http://openhardware.wordpress.com/ openhardware.wordpress.com]: Here is my openhardware blog | ||
| + | *[http://linuxstamp.budgetdedicated.com/ ftp site]: Here you will find tools and images like the crosscompilier and a debian file system | ||
*[http://www.atmel.com/dyn/products/app_notes.asp?family_id=605 App notes]: for Atmel arm processors | *[http://www.atmel.com/dyn/products/app_notes.asp?family_id=605 App notes]: for Atmel arm processors | ||
| − | *[http:// | + | *[[Linuxstamp Mboard 1| Mborad 1]] for the Linuxstamp |
| − | *[http:// | + | *[http://wiki.emqbit.com/free-ecb-at91 ECB AT91] This is another open source project similar to the Linuxstamp. They have some [http://wiki.emqbit.com/wiki very good documentation]. |
| + | *[http://www.budgetdedicated.com/ Budgetdedicated] Graciously hosts our ftp [http://linuxstamp.budgetdedicated.com/ site] | ||
| − | == | + | == USB Info == |
| − | The | + | The AT91RM9200 has 2x USB host ports and 1x device port. I bring out one of the USB host ports directly from the chip to a USB A connector. There is also a mini USB B connector on the board this is connected to the FT232RQ (USB/serial converter) which in turn is connected to the debug serial port on the AT91RM9200. So the linuxstamp can be both a USB host and a USB device. |
| − | I | + | |
| − | + | The FTDI driver creates a device /dev/ttyUSB0, a character device (this is how the Linuxstamp shows up on the host system). You can read/write to it as if it was a terminal, tty, or serial port. Above section on "Minicom & the debug port" points to communicating with the linuxstamp from a host computer. The FTDI232 chip connects to the mini-USB port. | |
== Discussion == | == Discussion == | ||
| + | Please join the google group for the Linuxstamp discussion | ||
| + | http://groups.google.com/group/linuxstamp | ||
| − | + | == Contact == | |
| − | + | For further questions or comments please contact Paul (pthomas8589 _at_ gmail _dot_ com) | |
| − | + | == other boards that run Linux == | |
| − | |||
| − | + | * [[ARMUS Embedded Linux Board]] | |
| − | : | + | * [http://balloonboard.org/ Balloon board] |
| − | + | * [http://www.bifferos.com/ Bifferboard] | |
| − | + | * [[Linuxstamp II 9260]] | |
| − | : | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Projects]] | [[Category:Projects]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:29, 14 December 2012
Contents
- 1 Description
- 2 Status
- 3 Features
- 4 License
- 5 Hardware design files
- 6 Power
- 7 Minicom & the debug port
- 8 nfs & tftp
- 9 Cross Compiler
- 10 Booting
- 11 U-boot
- 12 Busybox
- 13 Building the Linux Kernel
- 14 Minimal filesystem
- 15 Debian
- 16 Ptxdist
- 17 Dropbear SSH
- 18 802.11 Wireless Networking
- 19 GPIO / Hardware Pin I/O
- 20 Servos
- 21 Links
- 22 USB Info
- 23 Discussion
- 24 Contact
- 25 other boards that run Linux
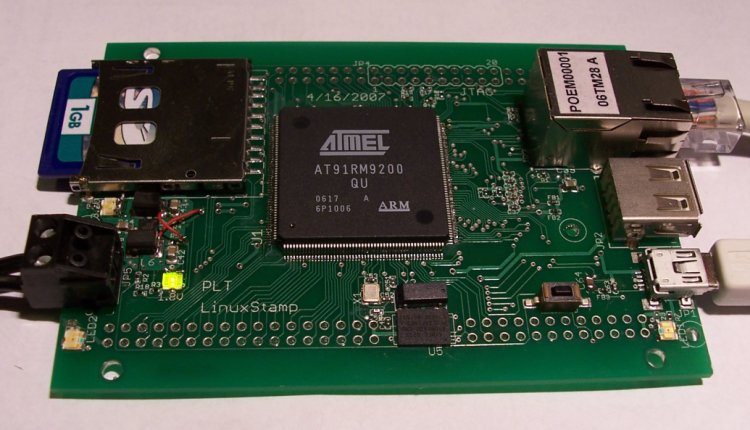
Description
The Linuxstamp is designed to be a general purpose processor module. It is designed to work as a stand alone module (SD card, Ethernet and USB/Serial converter are all on the module). This allows all initial development to be done without a motherboard, but for integration into a specific project a motherboard with specific features could be designed. Check out the start of the first mother board for the Linuxstamp, Mboard 1.
Status
You can now purchase Linuxstamp boards from thelinuxstamp.com
Features
- Atmel AT91RM9200 processor (Arm9 processor with MMU, 180Mhz operation)
- 32MB SDRAM (Only limited by 1x 54-TSOP SDRAM chip)
- 8MB SPI Dataflash
- 1x 10/100 Ethernet
- 1x USB host port (allows wifi adapters, flash drives and other USB devices to be used)
- 1x SD card slot
- Serial debug port access through FTDI USB/Serial converter
- JTAG port
- 2-Layer PCB design
- POE capable (48v -> 5v Power supply can be implemented on a motherboard)
License
All files for this project are licensed under the GNU GPL V2
Hardware design files
Warning!!! Use this design at your own risk.
If you want to use the Linuxstamp for your project you can get an Eagle library file here or just an image here
Power
The power supply for the board is based on the Linear LTC3407-3. This is a very compact high frequency switching power supply. It has both a 3.3v and a 1.8v output. It does have a very tight input range 3.3v-5.5v. The Micrel PHY also needs 2.5v, but this is provided by an internal regulator. Currently a regulated 5v must be used to power the board. Talking with Jeff from Jendy Labs it seems like POE (Power Over Ethernet) is a good idea. Wikipedia has a good general description of POE. The basic idea is that POE provides 48v and up to 13 watts, more than enough power for the Linuxstamp. The problem for the module is that a 48v -> 5v power supply is not small or cheap. In order to take advantage of POE without increasing the board size I found a part from Transtek Magnetics that is made for POE and has the rectifier built into the jack. The 48v lines are then connected to the pin header. This will allow a motherboard to integrate a POE power supply.
Minicom & the debug port
The mini-USB device port on the Linuxstamp does not connect directly to the AT91RM9200 it connects to the FT232R chip. The FT232R is a USB/serial converter. The FT232R chip has drivers for both Windows and Linux, but the Linux drivers are included in later kernels. Drivers for Mac OS X are available here.
When you plug the Linuxstamp into your host (Linux) machine a device should appear /dev/ttyUSB0 (I think the postfix number will increment as you add more devices). /dev/ttyUSB0 will behave as any other serial port now. Minicom is the standard program to access the serial port in Linux. The first time you run minicom you will have to be root in order to do the setup, after that you can change the permissions on /dev/ttyUSB0 so any user can run minicom. To enter configuration mode in minicom type CTRL-A o, now scroll down to Serial port setup. Use the letters to navigate. You will want the device to be /dev/ttyUSB0 and Bps/Par/Bits to read 115200 8N1. Both hardware and software flow control should be OFF. Connection to the board is important for loading Atmel's tiny program and u-boot, but once the board is working it might not be as important.
The default installation of minicom does not automatically include the XModem file transfer module 'sx' which you will need to send files. It is part of the Linux package named lrzsz (lrzsz). Just type 'sx' at a command line to see if it is installed. If not, install the lrzsz package and minicom will find and use 'sx' automatically.
XModem transfers between Minicom and U-Boot seem to work fine. This means that you can update U-Boot itself as well as the kernel and root file systems using Minicom after getting U-Boot itself installed via the built-in hardware bootloader in the AT91RM9200. The bootloader is much more finicky than U-Boot itself, so getting U-Boot installed can be tricky. Here is my technique:
- Connect the USB cable to LinuxStamp and start minicom from a terminal window.
- Boot the LinuxStamp. You should see CCC... on the minicom console, with a new C every second or two.
- Hit Enter twice. This will stall the bootloader, and the CCC... sequence will stop. It will also synchronize the USB/serial converter.
- Hit Ctrl-A Z S sequence to bring up the file transfer dialog in minicom. Select XModem and navigate to and select your u-boot.bin file (space bar).
- Hit Enter to start the xmodem transfer in minicom.
- Press and release the reset pushbutton on the LinuxStamp. The transfer should happen very quickly (a few seconds).
- Immediately hit Enter twice when you see the transfer complete. You *must* do this very quickly (within 1 second or so), and you *must* hit Enter twice. The first time exits the minicom file tranfer dialog, and the second time stalls the newly-loaded U-Boot program so that it doesn't try to auto-run the not-yet-loaded Linux kernel image.
You now have U-Boot in RAM, but not yet in flash. However, U-Boot is a lot nicer than the hardware bootloader, so you can now use U-Boot to load itself into flash by using the U-Boot menu and retransferring the u-boot.bin file again. This second time, the transfer will end up in flash, and will persist through poweroff/on.
Another alternative is to use HyperTerm on Windows, which works fine with the Hardware boot loader. If you are updating the Darrel Bootloader, note that the loader only has a short delay after you initiate the "receive" (on the loader) after which it send out the "ready to receive" signal. As a result, you'll need to be rather quick to initiate the Xmodem "send" (on HyperTerm). If you are seeing time outs on HyperTerm when you try and send the loader.bin file, you are probably hitting this problem ... you need to have initiated the send before you see the "C" on the screen from the bootloader.
nfs & tftp
Nfs (network file system) and tftp (trivial file transfer protocol) are two servers you will want running on your host machine. Nfs is useful for hosting the root file system of the Linuxstamp. Tftp is useful for u-boot to retrieve the kernel from. There are many other websites on nfs and tftp, but I will try and go over a simple setup. I would suggest being behind a firewall before trying either of these setups as neither is secure. I wrote this using a Fedora 7 system. First make sure you have nfs installed.
$ yum install nfs-utils nfs-utils-lib portmap system-config-nfs
On Ubuntu (or other debian-style systems) you could use:
$ sudo apt-get install portmap nfs-kernel-server nfs-common
Now to make sure the service is enabled run (this won't work on Ubuntu):
$ serviceconf and make sure nfs and nfs lock are checked
Now edit /etc/exports you should add a line like this /path_to_nfs_root/ *(rw,no_root_squash,insecure). Now restart nfs.
$ sudo /etc/init.d/nfs restart
You can test that it is set up correctly by typing the following on the local system (i.e. right on the NFS server)
$ showmount -e localhost
You can test this from a remote system with
$ mount -t nfs server_name:/path_to_nfs_root /path_to_test_mount
Now on to tftp. Make sure it is installed.
$ yum install tftp-server
This will create a file /etc/xinetd.d/tftp. In this file you will want to change disable from yes to no. Now make a test file.
$ cd /tftpboot $ echo hello > file
Now we can test it
$ tftp -v server_name -c get tmp
Now with u-boot we can load image files
> tftpboot 20800000 uImage
And boot them
> bootm 20800000
Cross Compiler
In order to compile for the AT91RM9200 we need to build a cross compilier. Dan Kegel has created a very useful tool for building a cross compiler. I am using Fedora 6 (x86_64) as my host system. After downloading and extracting crosstool (I was using version 0.43) I made two small changes. In the "demo-arm.sh" file I changed the eval line to
- "eval `cat arm.dat gcc-3.4.5-glibc-2.3.6.dat` sh all.sh --notest"
In the "arm.dat" file I changed the TARGET to "arm-linux" (By default u-boot looks for arm-linux-* tools). Now if you run "demo-arm.sh" you should get a cross compilier.
On Debian-style-systems you need to run something like apt-get install build-essential bison flex to get the above to work.
Booting
The AT91RM9200 has several features the facilitate easy booting. There is a good description of the booting order here. Atmel provides a tiny program that lives in the Dataflash and loads u-boot (see next section).
U-boot
First we need u-boot (doc) source (git) (formerly on sourceforge) (I was using version 1.1.6 - this is an old version). If you have not yet built a cross compilier now would be a good time to do so (See the cross compilier section above). Now you can do a test for the Atmel AT91RM9200 DK board.
- $ make at91rm9200dk_config
- $ make
This should give you a "u-boot.bin" file. We will have to write a board specific configuration file for the Linuxstamp. We should be able to base it off the the Atmel DK board. If you look at "/u-boot-1.1.6/include/configs/at91rm9200dk.h" you can see the configuration for the DK board.
Other u-boot commands:
- > printenv, prints the enviroment variables
- > saveenv, saves the enviroment variables
- > setenv bootcmd 'tftpboot 20800000 uImage; bootm 20800000' Sets the boot command to load a image over tftp and boot it
- > setenv bootargs mem=32M nfsroot=192.168.0.3:/nfs_root ip=192.168.0.51 console=ttyS0,115200n8 rootdelay=1
This sets the command line to be passed to the kernel. As you can see it sets the nfsroot, ip address and console
Busybox
Busybox provides the necessary utilities (e.g ls, cp, etc...). After you have downloaded and unpacked busybox we are ready to get started (I was using version 1.4.2).
- $ make defconfig
Now for a quick test we can make busybox for our host machine
- $ make
After you run this you should have a file 'busybox'. Now try
- $ ./busybox ls
But we want to build busybox for our embedded system so run
- $ make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
If you want to make Busybox with all the symbolic links for the tools run
- $ make CONFIG_PREFIX=/path_to_dir ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install
Building the Linux Kernel
If you have ever built the kernel for your desktop, then cross-compiling the kernel isn't that much harder. First get the latest kernel from kernel.org (I was using 2.6.23-rc9), then get the AT91RM9200 patch from here. After you unpack both of these you can apply the patch. From a Fedora 11 Live install you need the following packages: gcc, gcc-c++ and qt3-devel (for xconfig).
- $ patch -p1 < 2.6.23-rc3-at91.patch
Now lets take a look at the default configurations
- $ make ARCH=arm help
The ecbat91 is the closest to the linuxstamp.
- $ make ARCH=arm ecbat91_defconfig
If we what to further customize the build we can use 'xconfig'
- $ make ARCH=arm xconfig
Now we're are ready to build the kernel. You will have to have the u-boot tool mkimage in the PATH for this to work
- $ make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- uImage
If you want to build the modules you can do
- $ make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- modules
And then if you want to install the modules to an an NFS root or somewhere else do
- # make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- modules_install INSTALL_MOD_PATH=/path_to_nfs_root/
Minimal filesystem
There isn't much you need for a minimal filesystem. I suggest creating a staging area to create the filesystem. First you need the libraries generated by the cross compiler. On my machine they are located at /opt/crosstool/gcc-3.4.5-glibc-2.3.6/arm-linux/arm-linux/lib. Next you will need busybox, and we saw in the busybox section we can tell busybox where to output the files (use the root directory of your staging area). The last file we need is /dev/console.
- $ mkdir /staging_path/dev
/dev/console is a special file used to bind a device driver to a file. As such we use the mknod command.
- $ mknod /staging_path/dev/console c 5 1
The c says this is a character device. The 5 is the major node, and the 1 is the minor node.
For development the most convenient way to work is by mounting an NFS root file system. Another easy way to deal with the root file system is by mounting it on either a USB drive or SD card, but if you want a stand alone system you will want the root filesystem to come from the onboard Dataflash. There are several steps to do this. The Dataflash on the Linuxstamp is 8MB. A little under 2MB is used for the bootloaders and the Linux kernel. This leaves about 6MB for the filesystem. The filesystem I am working with is about 10MB, so we will need to compress the filesystem. One method of doing this is to use the initramfs function in the kernel. The kernel expects the image to be a gzipped CPIO archive. In the kernel source there are tools to create the CPIO archive. First we must create a file list from our file system (presumedly this is just the root of your current NFS mount).
/!!Remember that you need a 'init' file in /. You can just link to /sbin/init
- $ cd /path_to_linux_source
- # scripts/gen_initramfs_list.sh /path_to_fs_root/ > cpio_list
Next create the CPIO archive
- # usr/gen_init_cpio cpio_list > initramfs.cpio
You might have to make gen_init_cpio (in the usr dir)
- # make gen_init_cpio
Gzip the CPIO archive
- $ gzip initramfs.cpio
Now copy initramfs.cpio.gz to usr/initramfs_data.cpio.gz, and run the normal kernel make. You will notice that uImage is much larger (size = kernel + fs).
Debian
If want the full Linux enviroment your used to then you can try out Debian on the Linuxstamp. A working Debian filesystem can be found on the ftp site.
Ptxdist
If you looking for more features than the minimal filesystem, but don't need the full Debian system then ptxdist is right for you. The folks over at Pengutronix have done a very good job creating Ptxdist, a simple tool for building an embedded Linux distribution. If you want to test it out with the Linuxstamp, you can grab a build of the filesystem and kernel. If you want to try out ptxdist yourself, you can get the Linuxstamp project here.
Dropbear SSH
One of the first non busybox tools you will want is SSH. Dropbear is a small SSH client/server. I was able to get version 0.50 working.
- $ ./configure --host="arm-linux" --disable-zlib --prefix=/staging_path
- $ make all
- # make all install
You will have to make the device nodes /dev/ptmx and /dev/tty
- # mknod /dev/ptmx c 5 2
- # mknod /dev/tty c 5 0
You will also have to have the devpts filesystem mounted.
802.11 Wireless Networking
With the 2.6.27 vanilla kernel the ralink USB driver works very well. I've been using the AZIO AWU254 without any problems.
GPIO / Hardware Pin I/O
If you need some guidance figuring out how to 'bit twiddle' the GPIO (General Purpose I/O) pins on the at91 processor, here is a simple example with make file. If you have your arm-linux cross compiler configured with CrossTool just unpack this file into a folder and type 'make' to generate the executable binary.
This example shows how to set and clear output pins read input pins.
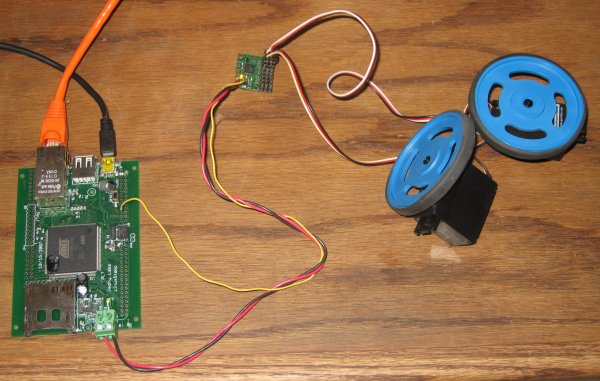
Servos
It is very easy to use the Linuxstamp with a RC servo controller like this one from pololu. In this setup the board is powered from the USB connector, so I was able to use the power terminal to power the pololu module. On the under side of the pololu module I connected the servo power with the chip power. The only other thing that is needed is the serial TX line from the Linuxstamp (yellow wire). I created a very simple program to run the servos. The following example would set servo 0 to a speed of 54 (64 is stopped) with an acceleration of 2.
- # ./servo_ser 0 2 54
Links
- Atmel: AT91RM9200 info on Atmel's site
- [1]: Up to date kernel patch for the AT91RM9200
- Cadsoft.de: Free (as in beer) tools for schematic and PCB design
- openhardware.wordpress.com: Here is my openhardware blog
- ftp site: Here you will find tools and images like the crosscompilier and a debian file system
- App notes: for Atmel arm processors
- Mborad 1 for the Linuxstamp
- ECB AT91 This is another open source project similar to the Linuxstamp. They have some very good documentation.
- Budgetdedicated Graciously hosts our ftp site
USB Info
The AT91RM9200 has 2x USB host ports and 1x device port. I bring out one of the USB host ports directly from the chip to a USB A connector. There is also a mini USB B connector on the board this is connected to the FT232RQ (USB/serial converter) which in turn is connected to the debug serial port on the AT91RM9200. So the linuxstamp can be both a USB host and a USB device.
The FTDI driver creates a device /dev/ttyUSB0, a character device (this is how the Linuxstamp shows up on the host system). You can read/write to it as if it was a terminal, tty, or serial port. Above section on "Minicom & the debug port" points to communicating with the linuxstamp from a host computer. The FTDI232 chip connects to the mini-USB port.
Discussion
Please join the google group for the Linuxstamp discussion http://groups.google.com/group/linuxstamp
Contact
For further questions or comments please contact Paul (pthomas8589 _at_ gmail _dot_ com)