Difference between revisions of "Printed Circuit Boards"
(yet another discussion of split ground plane) |
(mention power distribution networks (PDNs), with references.) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=== Software Design === | === Software Design === | ||
See [[software tool#Software_design_tools|Software Design Tools]]. | See [[software tool#Software_design_tools|Software Design Tools]]. | ||
| + | "gEDA", [https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Kicad "Kicad"], and "Eagle" are popular low-cost PCB layout tools. | ||
==== Step by Step by using Software Design Tool ==== | ==== Step by Step by using Software Design Tool ==== | ||
| − | *make sure the dimension and shape of PCB | + | *make sure the dimension and shape of the printed circuit board (PCB). |
| − | *make sure the size and location of | + | *make sure the size and location of mounting holes for PCB stand (typically 0.125" in diameter in all four corners) |
| − | *Make sure each components footprint. | + | *make sure the size and orientation of any ports / connectors / LEDs / etc. (if any) that need to be physically located in a specific location on the PCB. |
| + | |||
| + | (The above steps are dealing with the [[form factor]] of the PCB. | ||
| + | Sometimes we design a PCB without restrictions and then later we design the physical space around it. | ||
| + | But far more often, | ||
| + | we design new PCBs to cram into | ||
| + | some pre-existing space | ||
| + | with pre-existing mounting holes and interfaces. | ||
| + | ). | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Make sure each components footprint. [[PCB Footprints]]. | ||
*each components are placed on suitable place by put on a hardcopy of simulation PCB | *each components are placed on suitable place by put on a hardcopy of simulation PCB | ||
*All components get enough clearance between them. | *All components get enough clearance between them. | ||
| + | |||
| + | (By this point, we know roughly how big the PCB needs to be to support all the components and connectors. | ||
| + | We may decide pick some standard-size [[form factor]] in order to use commonly available boxes and other enclosures, rather than needing a custom-designed enclosure. | ||
| + | ). | ||
| + | |||
*Silkscreen layout is confirmed. | *Silkscreen layout is confirmed. | ||
*PCB is drawn. | *PCB is drawn. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 44: | ||
* [[Eagle Links]]Lots of links to the Eagle design tool. | * [[Eagle Links]]Lots of links to the Eagle design tool. | ||
* [http://www.electricstuff.co.uk/pcbs.html "How to make really really good homemade PCBs"] by Mike Harrison 2007 | * [http://www.electricstuff.co.uk/pcbs.html "How to make really really good homemade PCBs"] by Mike Harrison 2007 | ||
| + | * [http://paulwanamaker.wordpress.com/perfect-single-or-double-sided-pcbs-with-the-toner-transfer-method/ "Perfect Single or Double Sided PCBs with the Toner transfer Method"] by Paul Wanamaker 2012 | ||
| + | * [http://paulwanamaker.wordpress.com/300-2/ "DIY Copper Riveted Vias"] by Paul Wanamaker 2012 | ||
* [http://www.esmonde-white.com/home/diversions/etching-a-copper-pcb "Etching PCBs using Toner Transfer"] and [http://www.esmonde-white.com/home/diversions/milling-a-copper-pcb "Milling PCBs"] by Francis Esmonde-White, includes information on how to go from Eagle PCB to the etching or milling step | * [http://www.esmonde-white.com/home/diversions/etching-a-copper-pcb "Etching PCBs using Toner Transfer"] and [http://www.esmonde-white.com/home/diversions/milling-a-copper-pcb "Milling PCBs"] by Francis Esmonde-White, includes information on how to go from Eagle PCB to the etching or milling step | ||
* [[Toner Transfer]] -- This method involves laser printing your PCB design onto paper, then transferring toner onto copper-clad board. | * [[Toner Transfer]] -- This method involves laser printing your PCB design onto paper, then transferring toner onto copper-clad board. | ||
| Line 123: | Line 141: | ||
\ \------------ TX+ | \ \------------ TX+ | ||
\------------- TX- | \------------- TX- | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Power distribution network === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [FIXME: mention a few words about this earlier in this document?] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The power distribution network (PDN) ... | ||
| + | [FIXME: say a few words about distributing power to a bunch of separate PCBs] | ||
| + | [FIXME: say a few words about "one big voltage regulator" vs. "a bunch of little voltage regulators'] | ||
| + | [FIXME: say a few words about the PDN on a single PCB, soft-start inrush current, power sequencing, bypass capacitors, etc.] | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
| + | * [http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Practical_Electronics/PCB_Layout "Practical Electronics/PCB Layout"] has more tips on PCB layout | ||
*Grounding | *Grounding | ||
**[http://www.hottconsultants.com/pdf_files/june2001pcd_mixedsignal.pdf Partitioning and Layout of a Mixed Signal PCB]: The importance of single ground plane and partitioning of analog and digital signal trace | **[http://www.hottconsultants.com/pdf_files/june2001pcd_mixedsignal.pdf Partitioning and Layout of a Mixed Signal PCB]: The importance of single ground plane and partitioning of analog and digital signal trace | ||
| Line 146: | Line 174: | ||
** [http://www.st.com/stonline/books/pdf/docs/4967.pdf AN901: EMC guidelines for microcontroller-based applications] | ** [http://www.st.com/stonline/books/pdf/docs/4967.pdf AN901: EMC guidelines for microcontroller-based applications] | ||
** [http://www.st.com/stonline/books/pdf/docs/9914.pdf AN1709: EMC design guide for ST microcontrollers] | ** [http://www.st.com/stonline/books/pdf/docs/9914.pdf AN1709: EMC design guide for ST microcontrollers] | ||
| + | * Power distribution network | ||
| + | ** Pooja Mitra. [https://www.protoexpress.com/blog/common-pdn-design-challenges-and-how-to-resolve/ "4 Common PDN Design Challenges and How to Resolve Them"] | ||
| + | ** [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_network_design_(IC) Wikipedia: Power network design (IC)] | ||
| + | ** [https://www.ti.com/lit/an/sprac76g/sprac76g.pdf "TI Application Note: Sitara Processor Power Distribution Networks: Implementation and Analysis"] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:25, 19 September 2025
Printed circuit board design/fabrication
Overview
Software Design
See Software Design Tools. "gEDA", "Kicad", and "Eagle" are popular low-cost PCB layout tools.
Step by Step by using Software Design Tool
- make sure the dimension and shape of the printed circuit board (PCB).
- make sure the size and location of mounting holes for PCB stand (typically 0.125" in diameter in all four corners)
- make sure the size and orientation of any ports / connectors / LEDs / etc. (if any) that need to be physically located in a specific location on the PCB.
(The above steps are dealing with the form factor of the PCB. Sometimes we design a PCB without restrictions and then later we design the physical space around it. But far more often, we design new PCBs to cram into some pre-existing space with pre-existing mounting holes and interfaces. ).
- Make sure each components footprint. PCB Footprints.
- each components are placed on suitable place by put on a hardcopy of simulation PCB
- All components get enough clearance between them.
(By this point, we know roughly how big the PCB needs to be to support all the components and connectors. We may decide pick some standard-size form factor in order to use commonly available boxes and other enclosures, rather than needing a custom-designed enclosure. ).
- Silkscreen layout is confirmed.
- PCB is drawn.
- silkscreen adding the following:
- version no.
- organization name
- board name
- Netlist is ran and got a no error result.
- DRC is ran and got a no error result.
- Overall is checked.
- generate Gerber and send to PCB Manufacturers.
Manual Design
Some people do PCB layout on clear film or by directly drawing on a circuit board, of even by scratching, grinding.... For now let them google this.
Homebrew fabrication
Before exploring these techniques, you should understand your options with regard to services such as BatchPCB.com, ExpressPCB.com and PCB123.com. Being able to have several boards fabbed in 2 days for $59 (for example) makes it harder to justify the hassle of etching your own boards at home.
- Eagle LinksLots of links to the Eagle design tool.
- "How to make really really good homemade PCBs" by Mike Harrison 2007
- "Perfect Single or Double Sided PCBs with the Toner transfer Method" by Paul Wanamaker 2012
- "DIY Copper Riveted Vias" by Paul Wanamaker 2012
- "Etching PCBs using Toner Transfer" and "Milling PCBs" by Francis Esmonde-White, includes information on how to go from Eagle PCB to the etching or milling step
- Toner Transfer -- This method involves laser printing your PCB design onto paper, then transferring toner onto copper-clad board.
- Photoetching -- Exposure of PCB designs onto photosensitized copper-clad board.
- Chemical Etchants
- "Mechanically etching or milling PCBs. No chemicals!" -- Use your CNC router/mill to make PC boards.
- Open Source Ecology wiki: "Routed Circuit Board"
- Yahoo group: Homebrew_PCBs · Homebrew Printed Circuit Boards
- RepRap wiki has details on how to use open-source RepRap-based desktop routers to cut PCBs out of copper-clad board.
- "pcbprt - Experiments in inkjet PCB printing" by pascal. Some inkjet printers can print directly CD and DVD. Pascal explains step-by-step how to get those printers to print on copper-clad FR4 to make reasonably good etch resist. The main trick seems to be baking the freshly-printed boards to dry out the ink and get the dyes/pigments to stick to the copper -- otherwise the water-based ink immediately washes off as soon as you drop the board in the etch tank.
- A few people have made "DIY Flex Circuits".[1]
Commercial PCB fabrication
- Submitting PCB's for fabrication -- Common processes for submitting PCB's for fabrication.
- PCB Manufacturers
- "PCB fabbing advice" by Chris Anderson 2008
Best Practices for PCB Layout
Theory
- Provide the easiest path (lowest impedance) for current to flow
- Return current tends to flow directly under signal trace (for PCB having ground plane)
- Inductance increases with length of traces
- Inductance increases with the area enclosed by signal trace and ground
- Prevent digital currents from contaminating analog currents
- Decouple high speed components
- Use ground loop avoidance techniques
Layer stack-up
1-layer, 2-layer, and 4-layer boards all have their advantages and disadvantages.
Many people recommend going to 4-layer boards when using high-speed digital logic, since that allows a solid ground plane that improves EMI/EMC.
See:
Nansen Chen, Hongchin Lin.
"A Two-Layer Board Intellectual Property to Reduce Electromagnetic Radiation".
They manage to directly connect a DDR SDRAM in a 66-pin TSOP package
to a digital LCD-TV controller,
both on the top layer of a 2-layer PCB,
with
the DRAM CLOCK operating at about 250 Mbit/s and
the DRAM DQ operating at about 500 Mbit/s (DDR),
the Addr/CMD at about 125 Mbit/s,
playing 1080i video with picture in picture display.
Of the two very similar PCB layouts they present,
the one where the bottom layer to be a solid ground layer
under *all* the DRAM data and clock lines
produced significantly less EMI.
Design
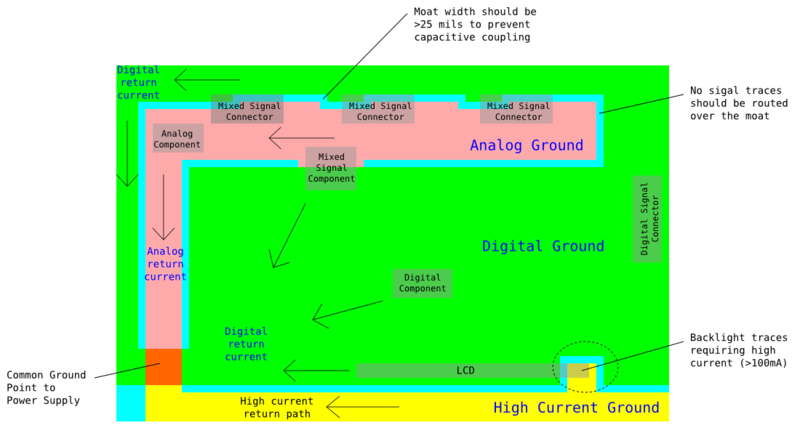
- Partition PCB into "analog stuff" and "digital stuff".
- No digital signal traces should cross over analog ground, and vice versa
- For components having both analog and digital signals (e.g. ADC), orientate components so that the analog signal traces goes only over the analog ground plane, and digital signal traces goes only over the digital ground plane
- AGND and DGND of ADC must have a small impedance (i.e. separated by short distance)
- Add decoupling capacitors close to Vcc and DGND of ICs
- Add ferrite beads and capacitors (PI-filter) to power rail for low-pass filtering (reduce ripples).
Routing
- Place fixed components first (components location that cannot be changed, e.g. connectors, buttons, etc)
- Make installing parts onto the PCB fast:
- Fastest: No through-hole parts. All surface-mount parts on the bottom side.
- Next-fastest: All through-hole parts on the top side. All surface-mount parts on the bottom side. ( "Mighty Mouse Main Printed Circuit Board (PCB)" )
- Separate components into groups
- Digital signals only
- Analog signals only
- Digital and analog (Mixed) signals
- High current devices (e.g. led backlight for LCD/buzzer)
- Do not partition ground into analog and digital planes.
- Use a single ground plane. See the " Grounding References" below.
- Orientate components that have mixed signals according to the orientation of the ground planes, and straddle components over DGND and AGND
- Place digital only components over DGND
- Place analog only components over AGND
- Decoupling capacitors should be as close to the ICs as possible
Vcc
| | | | |
+-----------+
-------+-+--|-+---------|-------- Vcc
|C| | IC |
-------+-+--|---------+-|-------- GND
+-----------+
| | | | |
GND
- Lay critical (noise-sensitive) traces first (e.g. crystal, analog signals)
- As short as possible
- Use 45o turnings instead of 90o
- Paired signal traces (e.g. TX+, TX- in ethernet chips) should run parallel along each other
TX+ -----\
TX- ----\ \
\ \
\ \
\ \
\ \------------ TX+
\------------- TX-
Power distribution network
[FIXME: mention a few words about this earlier in this document?]
The power distribution network (PDN) ... [FIXME: say a few words about distributing power to a bunch of separate PCBs] [FIXME: say a few words about "one big voltage regulator" vs. "a bunch of little voltage regulators'] [FIXME: say a few words about the PDN on a single PCB, soft-start inrush current, power sequencing, bypass capacitors, etc.]
References
- "Practical Electronics/PCB Layout" has more tips on PCB layout
- Grounding
- Partitioning and Layout of a Mixed Signal PCB: The importance of single ground plane and partitioning of analog and digital signal trace
- Massmind Techref: "Unsplit ground"
- Rob Reeder. "Mine These High-Speed ADC Layout Nuggets For Design Gold"[2] "Electronic Design" 2011. "Splitting Grounds: ... [should] the ground plane ... be split into an AGND and DGND ground plane when using an ADC [?] ... not usually. In most situations a split ground plane can cause more harm than good, as blindly splitting the ground plane only serves to increase the inductance for the return current."
- Ground- A Path For Current Flow: The importance of decoupling capacitors
- PCB Layout Tips: a power point presentation
- PCB Layout Guidelines: in Traditional Chinese
- Crystals and Oscillators
- AVR186: Best Practices for the PCB layout of Oscillators
- ADC & Analog Filters
- ADN007: Techniques that Reduce System Noise in ADC Circuits
- ADN010: Predict the Repeatability of your ADC to the BIT
- AD699: Anti-Aliasing, Analog Filters for Data Acquisition Systems
- AN682: Using Single Supply Operational Amplifiers in Embedded Systems
- AN990: Analog Sensor Conditioning Circuits - An Overview
- EMC
- AVR040: EMC Design Considerations
- AN1705: Noise Reduction Techniques for Microcontroller-Based Systems
- AN898: EMC general information
- AN901: EMC guidelines for microcontroller-based applications
- AN1709: EMC design guide for ST microcontrollers
- Power distribution network